Advancements in Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) Technology
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems have become the backbone of modern infrastructure. These systems, which were once a luxury,...

4D printing, an avant-garde advancement in the realm of additive manufacturing, is redefining the boundaries of what's possible in design and production.
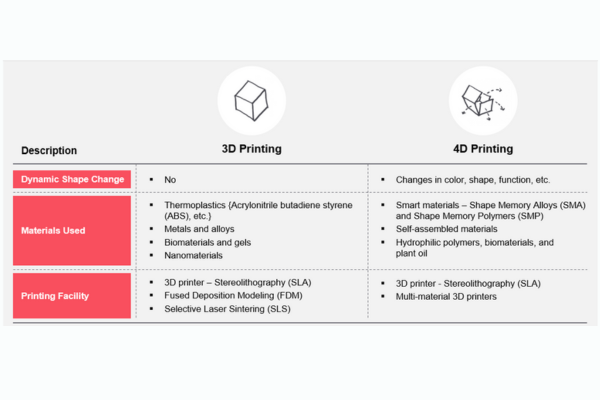
While 3D printing has already revolutionized industries by allowing for intricate designs and rapid prototyping, 4D printing introduces an entirely new dimension: time.
This transformative technology enables the creation of objects that can adapt, evolve, and change shape or properties over time in response to external stimuli, such as heat, light, humidity, or other environmental factors.
The term "fourth dimension" in this context is a nod to this transformative aspect of time, setting it apart from the static three spatial dimensions of traditional 3D printing.
Here are some key aspects of 4D printing that need to be taken into consideration.
At the heart of 4D printing lies the utilization of specialized, often groundbreaking materials. These "smart" or "programmable" materials are meticulously engineered to react to specific external stimuli:
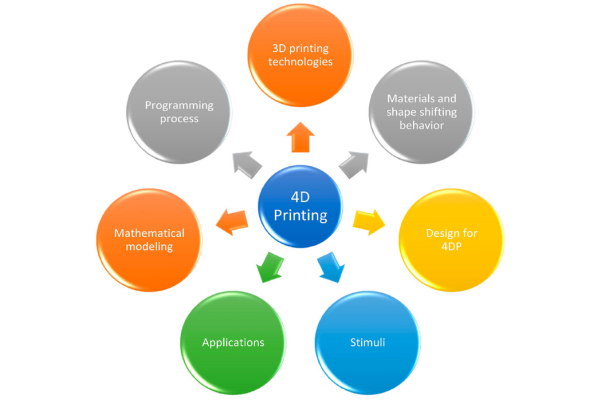
The design intricacies for 4D printing surpass those of traditional 3D printing. It demands not only the meticulous specification of the object's spatial geometry but also the intricate encoding of its evolutionary path over time.
This "programming" is seamlessly embedded within the material itself, guiding its reaction to specific stimuli, making the design process both an art and a science.
The true marvel of a 4D-printed object is its post-production metamorphosis. Picture a flat sheet that, upon contact with water, gracefully folds itself into a predetermined intricate shape, reminiscent of origami.
Such awe-inspiring transformations are the culmination of the unique properties of the materials used and the visionary design programming encoded within time.
The horizon of 4D printing applications is vast, touching multiple industries and promising paradigm shifts in design and utility.

Environmental Applications: Beyond human-centric applications, 4D printed devices could play pivotal roles in environmental monitoring and restoration, with tools that adapt properties to collect pollutants or signal shifts in environmental conditions.
The world of 4D printing, while promising, is still in its infancy. Researchers globally are investing immense intellectual capital into uncovering new materials and refining design methodologies to harness this technology's full potential.
4D Printing, though still in its developmental stages, holds a promise that's hard to ignore. As research intensifies and practical applications burgeon, we are on the cusp of a design and manufacturing renaissance. Objects of the future may not just be static entities but dynamic, adaptive systems, symbiotically interacting with and responding to their environment.

Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems have become the backbone of modern infrastructure. These systems, which were once a luxury,...

The Internet of Things (IoT) is not just a buzzword; it's a revolutionary technology that's reshaping our world. With its ability to connect billions...

In a world where access to quality education is often seen as a privilege, the Sri Aurobindo Institute of Technology (SAIT) stands as a beacon of...