3D Printing with Product Design
The advent of 3D printing has brought about a significant shift in the way product design is approached. 3D printing technology has revolutionized...

Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is the process of creating three-dimensional objects by layering materials on top of each other. The process is entirely computer-controlled, and the technology has come long since its inception in the 1980s.
Today, 3D printing has become an essential tool for many industries, from aerospace and automotive to healthcare and consumer products. In this blog, we'll explore additive manufacturing in 3D printing and its potential for the future.
The 3D printing process starts with a 3D model created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The software creates a digital model that can be sliced into thousands of layers, each printed individually. The printer then reads the sliced file and builds the object layer by layer.

There are several types of 3D printing technologies, but fused deposition modeling (FDM) is the most common. In FDM, the printer melts a plastic filament and extrudes it through a nozzle to build the object layer by layer. Other technologies include stereolithography (SLA), which uses a laser to cure a liquid resin, and selective laser sintering (SLS), which uses a laser to fuse powdered material together.
One of the biggest advantages of 3D printing is the ability to create complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to produce with traditional manufacturing methods. The technology allows for the creation of custom designs and shapes, which can be tailored to specific applications.
Another advantage is the speed of prototyping. In traditional manufacturing, creating a prototype can take weeks or even months, as tooling and moulds need to be created. With 3D printing, a prototype can be produced in a matter of hours or days, allowing for rapid iteration and design changes.
In addition, 3D printing is a more sustainable manufacturing method than traditional methods. Because it only uses the materials needed to create the object.
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from digital designs by adding material layer by layer until the final product is formed.
This technology has gained immense popularity recently due to its ability to produce highly customized and intricate designs quickly and cost-effectively. This blog will explore the world of additive manufacturing in 3D printing and its various applications.
The 3D printing process starts with a digital 3D model of the object created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The 3D model is then sliced into hundreds or thousands of layers; each sent to the 3D printer.
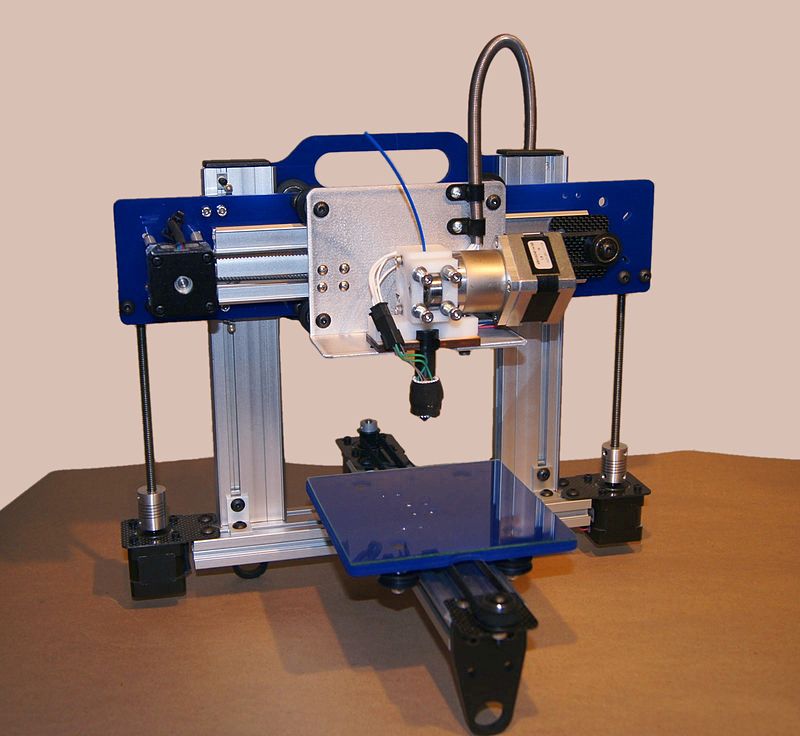
The printer then creates the object layer by layer, by depositing material such as plastic, metal, or ceramic, until the final product is formed. The process is highly precise, and the resulting object is an exact replica of the 3D model.
Compared to traditional manufacturing methods, additive manufacturing has its own advantages. One of the biggest advantages is that it allows for highly complex geometries that would be impossible to produce with traditional methods.
This property, in particular, helps open up new possibilities when considering product design and innovation. 3D printing also reduces the amount of waste generated during manufacturing, as only the necessary material is used to create the object. This makes 3D printing a more sustainable manufacturing option.
The applications of additive manufacturing are vast and diverse. In the medical field, 3D printing is used to create customized prosthetics, implants, and surgical tools. This allows for a higher level of personalization and accuracy in medical treatments. 3D printing is also used in the aerospace industry to create lightweight and complex parts for aeroplanes and rockets.
In architecture and construction, 3D printing is used to create large-scale models of buildings and other structures.
The automotive industry is also using 3D printing to produce prototypes and parts. This allows for faster design iterations and reduced time to market.
In the fashion industry, 3D printing is used to create unique and complex designs that would be difficult to produce with traditional methods. Additionally, 3D printing is used in education to teach students about product design and manufacturing.
Additive manufacturing in 3D printing is a game-changer for the manufacturing industry. Its ability to quickly create highly customized and intricate designs are cost-effectively transforming how products are made. With its diverse applications and advantages, 3D printing is set to become a critical manufacturing method for many industries in the years to come.
3D printing has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by enabling personalized prosthetics, implants, and medical devices. 3D printing can also create patient-specific models for surgical planning and training.
3D printing can enable mass customization of products at scale, which was previously impossible. This could lead to a shift from mass production to mass customization, allowing companies to cater to individual customer needs.
3D printing can reduce waste in manufacturing by enabling the precise production of parts and products, minimizing material waste. This could also lead to the use of more sustainable materials in manufacturing.
3D printing can produce parts and tools on demand in space, reducing the need for expensive and time-consuming resupply missions. This could be especially useful in long-term space missions.
3D printing is a key technology in the Fourth Industrial Revolution, or Industry 4.0- an era in the industrial revolution characterized by integrating digital and physical systems. 3D printing can enable the on-demand production of parts and products, reducing inventory costs and enabling agile manufacturing.
Overall, the future of 3D printing is bright, with potential applications in many industries and fields. As the technology continues to develop, we expect to see more innovations and advances to further enhance its capabilities and impact.

The advent of 3D printing has brought about a significant shift in the way product design is approached. 3D printing technology has revolutionized...
Engineering is a field that has contributed immensely to the development of modern society. Engineers design, build, and maintain the infrastructure...

In a world where access to quality education is often seen as a privilege, the Sri Aurobindo Institute of Technology (SAIT) stands as a beacon of...